Introduction :
On one of my recent Java projects I had to work with a character encoding other than the default ANSI encoding. Thus, I managed to set up the database connection properly to use the required UTF-8 encoding, as well as handle the returned data correctly as UTF-8 in the Java code.
When I tried to output some of the data, for logging purposes, in the console, the output couldn’t not be read correctly. The first thought was to double-check the source code, connection properties etc, and despite the fact that everything looked just fine, the console output still was unreadable.
The default character encoding in Java for MAC OS X is MacRoman. The default font encoding on some other platforms is ISO-Latin-1 or WinLatin-1; unlike MacRoman, these encodings are subsets of UTF-8. Programs that assume that filenames can be turned into UTF-8 by just turning a byte into a char will cause problems in MAC OS X.
The simplest way to work around this problem is to specify a font encoding explicitly rather than assuming one. Specifying a font encoding besides UTF-8 and UTF-16 is not recommended.
After spending some time trying to find a relevant answer in google, i came to know that it was indeed in Eclipse, everybody knows Eclipse is an excellent IDE, however some of its preferences may not be that straight-forward. I stumbled upon the “Common” tab in the Configurations panel. And indeed this is where I found the answer to the encoding problem!
Here is what you have got to do if you are having a similar issue:
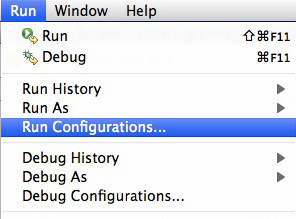
Go to Run -> Run Configurations..
or
Right Click on project -> Run As -> Run Configurations..
Create or select an existing configuration for your project, and switch to the “Common” tab.
Choose you preferred Encoding as shown on the image above!
You are done now..
If you do not specify a font encoding explicitly, recognise that:
Happy to help.. :)
References :
decoding.wordpress.com
Eclipse
On one of my recent Java projects I had to work with a character encoding other than the default ANSI encoding. Thus, I managed to set up the database connection properly to use the required UTF-8 encoding, as well as handle the returned data correctly as UTF-8 in the Java code.
When I tried to output some of the data, for logging purposes, in the console, the output couldn’t not be read correctly. The first thought was to double-check the source code, connection properties etc, and despite the fact that everything looked just fine, the console output still was unreadable.
The default character encoding in Java for MAC OS X is MacRoman. The default font encoding on some other platforms is ISO-Latin-1 or WinLatin-1; unlike MacRoman, these encodings are subsets of UTF-8. Programs that assume that filenames can be turned into UTF-8 by just turning a byte into a char will cause problems in MAC OS X.
The simplest way to work around this problem is to specify a font encoding explicitly rather than assuming one. Specifying a font encoding besides UTF-8 and UTF-16 is not recommended.
After spending some time trying to find a relevant answer in google, i came to know that it was indeed in Eclipse, everybody knows Eclipse is an excellent IDE, however some of its preferences may not be that straight-forward. I stumbled upon the “Common” tab in the Configurations panel. And indeed this is where I found the answer to the encoding problem!
Here is what you have got to do if you are having a similar issue:
Go to Run -> Run Configurations..
or
Right Click on project -> Run As -> Run Configurations..
Create or select an existing configuration for your project, and switch to the “Common” tab.
Choose you preferred Encoding as shown on the image above!
You are done now..
If you do not specify a font encoding explicitly, recognise that:
- In the conversion from a Unicode subset to MacRoman you may lose information.
- Filenames are not stored on disk in the default font encoding, but in UTF-8. Usually this isn’t a problem, because most files are handled in Java as java.io.Files, though it is good to be aware of.
- Although filenames are stored on disk as UTF-8, they are stored decomposed. This means that certain characters—for example, e-acute (é)—are stored as two characters, “e”, followed by “´” (acute accent). The default HFS+ filesystem of OS X enforces this behavior. SMB enforces composed Unicode characters. UFS and NFS do not specify whether filenames are stored composed or decomposed, so they can do either.
Happy to help.. :)
References :
decoding.wordpress.com
Eclipse

0 comments:
Post a Comment